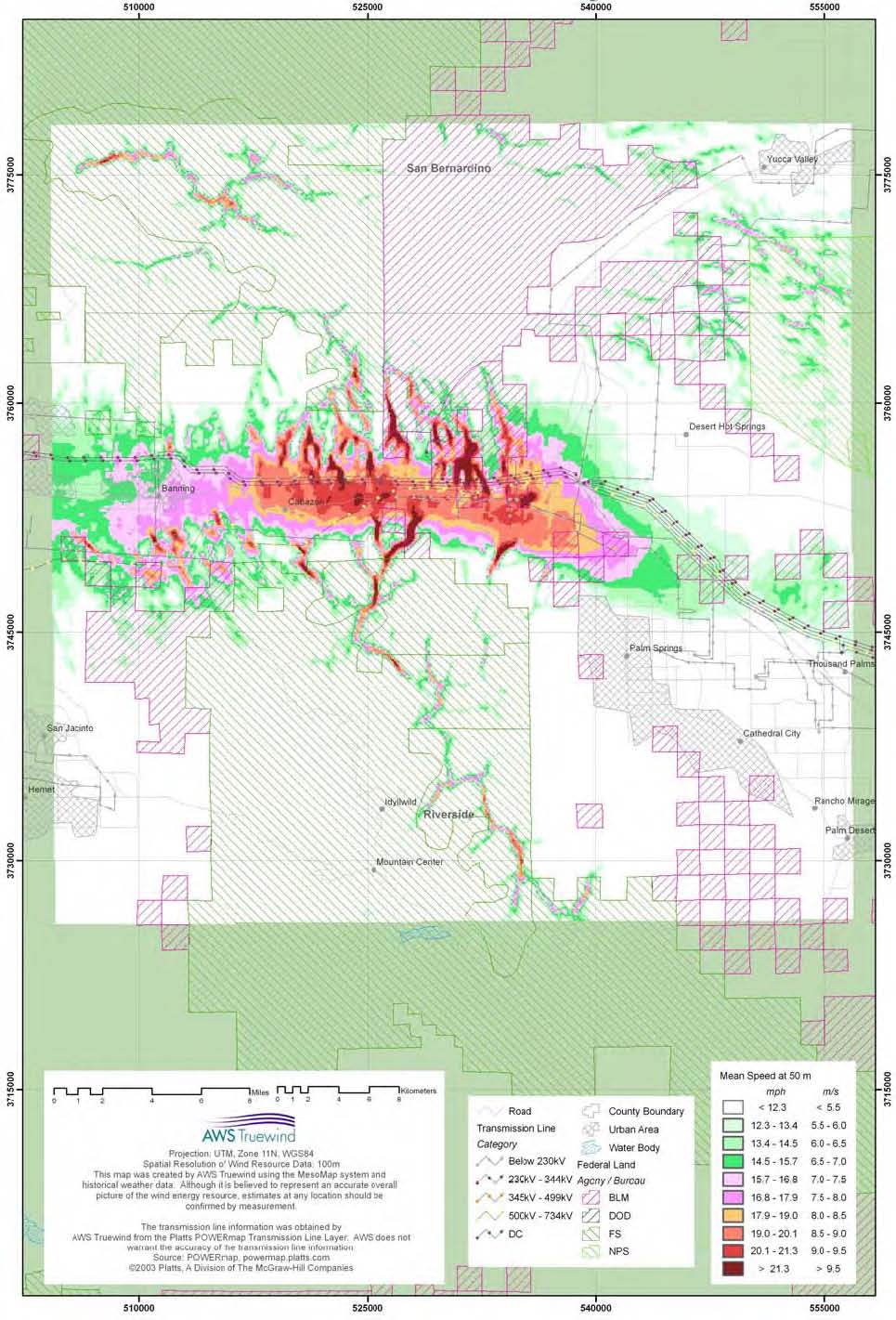
3.1 GW of short turbines could be added to the San Gorgonio Pass Wind Resource Area
Wind Harvest analyzed the San Gorgonio Pass Wind Resource Area using publicly available location information and UL’s Windnavigator. We found that the area could add 3,136 MWs of Wind Harvester type turbines to the existing 682 MWs of propeller-type turbines currently installed. Based on the mid-level wind speeds in the zone, this level of buildout would produce 10,040 GWh of electricity per year. The existing wind farms produce 2,661 GWh of electricity per year.